Galectin-3 is a new important factor and inflammatory marker in the development of patients with cardiovascular inflammation, progressive cardiovascular disease and heart failure. Inhibition (reduction) of galectin-3 slows down the progression of myocardial (heart muscle) inflammation, reduces collagen production, promotes cardiac remodeling and supports healthy cardiac function. Galectin-3 a β-galactoside-binding lectin shows to be a key marker and inflammatory factor in the process of intravascular inflammation. Strong evidence shows that Galectin-3 participates in the initiation and progression of arteriolosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), endothelial (inner lining of the blood vessels) dysfunction and concurrent vascular inflammation. Amplification of cardiovascular, neurological and systemic inflammation are the most important galectin-3 mechanism.
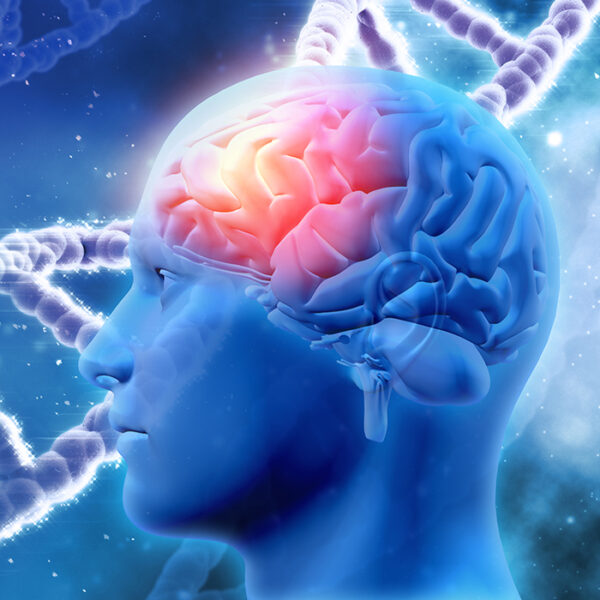
Brain inflammation and progressive damage is the most common cause of dementia and Alzheimer’s as well as other neurological/brain conditions and is characterized by the deposits of extracellular aggregates of amyloid plaque and the formation of neurofibrillary tangles. Neurofibrillary tangles are twisted fibers found inside the brain’s cells. These tangles consist primarily of a protein called tau. These tangles are concurrent with the progression of microglial activation and neuroinflammation. Microglia, the resident innate immune cells in the brain, have long been implicated in the pathology of neurodegenerative diseases by driving progressive neuron damage. One of the key molecules involved in microglial activation is galectin-3 (Gal-3). In recent years, extensive studies have dissected the mechanisms by which Gal-3 modulates microglial activation (Microglia is the resident innate immune cells in the brain), The emerging role of Galectin-3 in biology and pathobiology, including its origin, its functions in regulating microglial activation and its key role in the upregulation of neuroinflammation and its emergence as a biomarker in other neurodegenerative diseases as well.
Further supporting the idea that Microglia, the resident innate immune cells in the brain, have long been implicated in the pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Accumulating evidence points to activated microglia as a chronic source of multiple neurological toxicity factors driving progressive neuron (nerve cell) damage. Microglia can become chronically activated by either a single stimulus or multiple stimuli exposures to result in cumulative neuronal loss over time. Galectin-3 relating to cardiac dysfunction is evidence that the delivery of galectin-3 can lead to collagen being deposited in the heart and these deposits can lead to progressive fibrosis (heart damage). Models showed that the level of galectin-3 associated strongly with the severity of future fibrosis in the heart. It also plays a significant role in fibrosis of other organs, including the liver and kidney. A major study also identified galectin-3 as a possible biomarker for patients with acute rapid onset of heart failure resulting in hospitalization or unplanned office or emergency room visits. Most of these episodes result from worsening of chronic heart failure.
By reviewing a wide body of literature one can conclude that Galactin-3 should be considered a valuable biomarker for any chronic inflammatory illness and its reduction may play an important role in how to better address these very common disorders. By addressing them before damage sets in is the key to better health and longevity. Support the reduction of galactin-3 and inflammation with CLINICAL SYNERGY PECTOL-C PROFESSIONAL powder or capsules.
This information has not been reviewed by the FDA and does not claim to cure, prevent, treat or diagnose any disease